比较器
数组是所有编程语言中重要的组成部分,而 Java 提供 3 数组的相关操作类。同时在 Java 中由于存在对象数组的概念,就可以利用比较器实现对象数组的比较操作。
Arrays 类
本书讲解数组时为读者讲解过一个数组排序的操作:java.util.Arrays.sort(数组名称) ,而在 Java 中,Arrays 是一个定义在 java.util 包中专门进行数组的操作类,在这个类中定义了所有与数组有关的基本操作:二分查找、相等判断、数组填充等,如表所示。
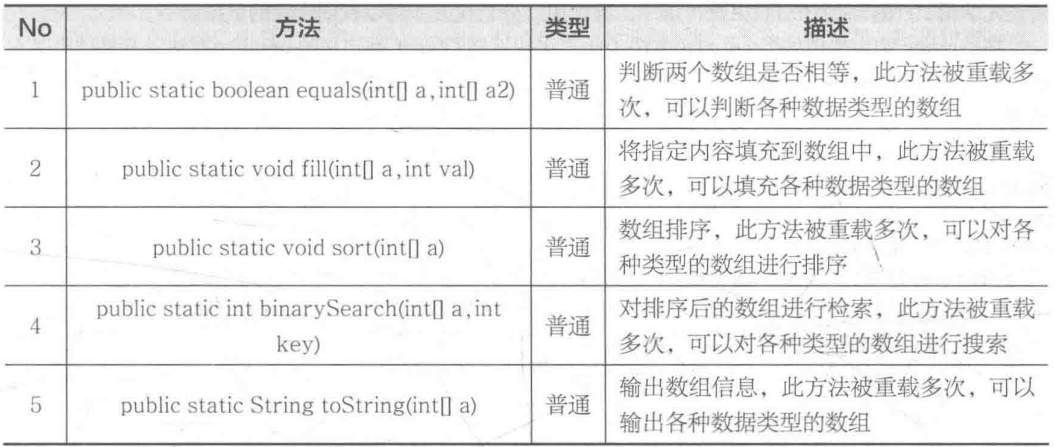
二分查找又被称为折半查找法,在进行数据查找时速度较快,而要使用二分查找法,则要求数组中的数据必须为有序的。二分查找法的基本原理如图所示。
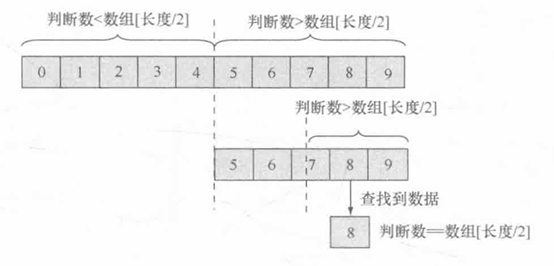
二分查找的基本思想是将 n 个元素的数组分成大致相等的两部分。假设要查找的数据内容为 x ,则取 数组长度/2 与 X 进行比较,如果 x=数组[长度/2] ,则表示存在 x ,算法中止;如果 x<数组[长度/2] ,则只要在数组的左半部分继续搜索 x ,如果 x>数组[长度/2],则要在数组的右半部搜索 X 。
package com.yootk.demo;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int data[] = new int[] { 1, 5, 6, 2, 3, 4, 9, 8, 7, 10 };
java.util.Arrays.sort(data); // 数组必须排序才可以查找
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(data, 9));
}
}package com.yootk.demo;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int data[] = new int[] { 1, 5, 6, 2, 3, 4, 9, 8, 7, 10 };
java.util.Arrays.sort(data); // 数组必须排序才可以查找
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(data, 9));
}
}本程序首先定义了一个数组数据,但是由于此数据没有排序,所以无法使用二分查找算法。这样就需要先使用 Arrays.sort() 对数组进行排序,再使用二分查找时才可以找到指定的数据索引。在 Arrays 类中也提供了 equals() 方法(此方法并不是 Object 类定义的equals() 方法,只是借用了方法名称),利用此方法可以实现两个数组的相等判断,而要想使用此方法,就必须保证数组中的数据内容的顺序是一致的。
package com.yootk.demo;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int dataA[] = new int[] { 1, 2, 3 }; // 定义A数组
int dataB[] = new int[] { 1, 2, 3 }; // 定义B数组
System.out.println(Arrays.equals(dataA, dataB)); // 比较是否相等
}
}package com.yootk.demo;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int dataA[] = new int[] { 1, 2, 3 }; // 定义A数组
int dataB[] = new int[] { 1, 2, 3 }; // 定义B数组
System.out.println(Arrays.equals(dataA, dataB)); // 比较是否相等
}
}本程序中由于两个数组的内容顺序完全相同,所以最终的判断结果就是 true 。
Arrays 类还提供了数组的填充方法,即可以使用指定的数据为数组进行填充操作。
package com.yootk.demo;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int data[] = new int[10]; // 动态开辟数组
Arrays.fill(data, 3); // 填充数组数据
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data)); // 将数组变为字符串输出
}
}package com.yootk.demo;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int data[] = new int[10]; // 动态开辟数组
Arrays.fill(data, 3); // 填充数组数据
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(data)); // 将数组变为字符串输出
}
}本程序首先开辟了一个具备 10 个元素大小的数组空间,然后使用 10 方法进行填充,最后利用 Arrays 类中提供的 toString() 方法直接将数组变为指定格式字符串数据后输出。
比较器:Comparable
数组实际上会分为普通数组与对象数组两类使用情况,普通数组可以直接根据数据的大小关系进行排序(调用 Arrays.sort() 排序);而对象数组由于其本身存放的都是地址数据,不可能依据大小关系来实现排序,但是在 Arrays 类中依然重载了一个 sort() 方法(对象数组排序:public static void sort(Object[] a) ,此方法可以直接针对对象数组实现排序。要想使用 sort() 方法进行排序,就必须有一个前提:对象所在的类一定要实现 Comparable 接口,否则代码执行时会出现 ClassCastException 异常。而 Comparable 接口就属于比较器的一种,此接口定义如下。
public interface Comparable<T>{
public int conpareTo(T o)
}
在 Comparable 接口中只定义了一个 compareTo() 方法,此方法返回一个 int 型数据,而用户覆写此方法时只需要返回 3 种结果: 1(>0)、-1(<0)、0(=0)。
package com.yootk.demo;
import java.util.Arrays;
class Book implements Comparable<Book> { // 实现比较器
private String title ;
private double price ;
public Book(String title,double price) {
this.title = title ;
this.price = price ;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "书名:" + this.title + ",价格:" + this.price + "\n" ;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Book o) { // Arrays.sort()会自动调用此方法比较
if (this.price > o.price) {
return 1 ;
} else if (this.price < o.price) {
return -1 ;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Book books [] = new Book [] {
new Book("Java开发实战经典",79.8) ,
new Book("JavaWEB开发实战经典",69.8) ,
new Book("Oracle开发实战经典",99.8) ,
new Book("Android开发实战经典",89.8)
} ;
Arrays.sort(books); // 对象数组排序
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(books));
}
}package com.yootk.demo;
import java.util.Arrays;
class Book implements Comparable<Book> { // 实现比较器
private String title ;
private double price ;
public Book(String title,double price) {
this.title = title ;
this.price = price ;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "书名:" + this.title + ",价格:" + this.price + "\n" ;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Book o) { // Arrays.sort()会自动调用此方法比较
if (this.price > o.price) {
return 1 ;
} else if (this.price < o.price) {
return -1 ;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Book books [] = new Book [] {
new Book("Java开发实战经典",79.8) ,
new Book("JavaWEB开发实战经典",69.8) ,
new Book("Oracle开发实战经典",99.8) ,
new Book("Android开发实战经典",89.8)
} ;
Arrays.sort(books); // 对象数组排序
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(books));
}
}本程序在 Book 类定义时实现了 Comparable 接口,这样就意味着此类的对象可以实现对象数组的排序操作。在主类中使用 Arrays.sort() 方法时,会自动调用被 Book 类覆写的 compareTo() 方法判断对象的大小关系,这样就会按照价格由低到高进行排序。
优先考虑 Comparable
在 Java 中比较器有两种实现方式,其中,Comparable 是最为常用的比较器接口。在实际开发中,只要是对象数组排序,一定要优先考虑使用 Comparable 接口实现。
数据结构一BinaryTree
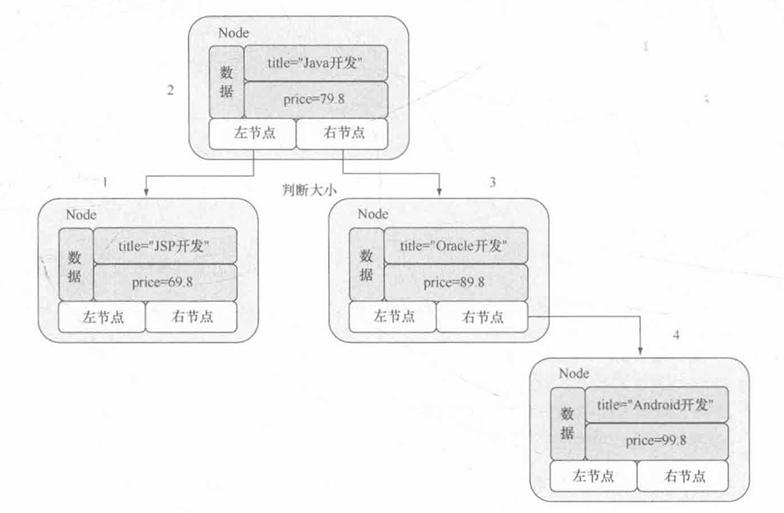
树是一种比链表更为复杂的概念应用,其本质也属于动态对象数组,但是与链表不同的是,树的最大特征是可以针对数据进行排序。树的操作原理:选择第一个数据作为根节点,而后比根节点小的放在根节点的左子树(左节点),比根节点大的数据放在右子树(右节点),取得数据时按照中序遍历的方式取出(左一中一右)。但是如果要想实现这样的排列,则需要有一个数据的包装类 Node ,而且在此类中除了要保存数据外,还需要保存对应的左子树以及右子树节点对象,如图所示。
根据自己的实际情况选择性学习
在实际的项目开发中,链表与树是使用最多的两种数据结构,所以一小部分公司会在笔试时要求应聘者编写出相应的代码。而从实际的开发角度来讲,常用数据结构已经被 Java 完整地实现好了,在类集框架中会为读者讲解,所以此处只是一个原理的简单分析。建议读者在掌握链表开发之后再进行学习。
二叉树数据结构的程序操作如下。
(1)定义出要使用的数据类型,并且类中一定要实现 Comparable 接口。
import java.util.Arrays;
class Book implements Comparable<Book> { // 实现比较器
private String title ;
private double price ;
public Book(String title,double price) {
this.title = title ;
this.price = price ;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "书名:" + this.title + ",价格:" + this.price + "\n" ;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Book o) { // Arrays.sort()会自动调用此方法比较
if (this.price > o.price) {
return 1 ;
} else if (this.price < o.price) {
return -1 ;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}import java.util.Arrays;
class Book implements Comparable<Book> { // 实现比较器
private String title ;
private double price ;
public Book(String title,double price) {
this.title = title ;
this.price = price ;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "书名:" + this.title + ",价格:" + this.price + "\n" ;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Book o) { // Arrays.sort()会自动调用此方法比较
if (this.price > o.price) {
return 1 ;
} else if (this.price < o.price) {
return -1 ;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}(2)定义二叉树,所有的数据结构都需要通过 Node 类的对象包装,同时为了排序需要,保存的数据可以直接使用 Comparable 接口类型,即所有的类对象都必须强制转换为 Comparable 接口。在本结构中只定义数据的保存和取出的操作方法。
@SuppressWarnings("rowtypes")
class BinaryTree {
private class Node {
private Comparable data; //排序的依据就是 Comparable
private Node left; //保存左节点
private Node right; //保存右节点
public Node(Comparable data) { //定义构造方法
this.data = data;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void addNode(Node newNode) {
if (this.data.compareTo(newNode.data) > 0) { //对象数据比较
if (this.data == null) { //左节点为null
this.left = newNode; //保存左节点
} else {
this.left.addNode(newNode); //继续判断节点保存位置
}
} else {
if (this.right == null) { //右节点为null
this.right = newNode; //保存右节点
} else {
this.right.addNode(newNode); //继续判断节点保存位置
}
}
}
public void toArrayNode() { //将节点转换为对象数组
if (this.left != null) { //表示有左节点
this.left.toArrayNode(); //左子树继续取得
}
// 先判断左节点再取出中间节点数据,再取得右节点数据
BinaryTree.this.retData[BinaryTree.this.foot++] = this.data;
if (this.right != null) { //表示有右节点
this.right.toArrayNode(); //右子树继续取得
}
}
}
private Node root; //定义根节点
private int count; //保存元素个数
private Object[] retData; //保存返回的对象数组
private int foot; //操作角标
public void add(Object obj) { //进行数据的追加
Comparable com = (Comparable) obj; //转为Comparable才可以实现Node保存
Node newNode = new Node(com); //创建新的节点
if (this.root == null) { //现在不存在节点
this.root = newNode; //保存根节点
} else {
this.root.addNode(newNode); //交给Node类处理
}
this.count++; //保存个数加一
}
public Object[] toArray() { //取得全部保存数据
if (this.root == null) { //根节点为null
return null; //没有数据
}
this.foot = 0;
this.retData = new Object[this.count];
this.root.toArrayNode();
return this.retData;
}
}@SuppressWarnings("rowtypes")
class BinaryTree {
private class Node {
private Comparable data; //排序的依据就是 Comparable
private Node left; //保存左节点
private Node right; //保存右节点
public Node(Comparable data) { //定义构造方法
this.data = data;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void addNode(Node newNode) {
if (this.data.compareTo(newNode.data) > 0) { //对象数据比较
if (this.data == null) { //左节点为null
this.left = newNode; //保存左节点
} else {
this.left.addNode(newNode); //继续判断节点保存位置
}
} else {
if (this.right == null) { //右节点为null
this.right = newNode; //保存右节点
} else {
this.right.addNode(newNode); //继续判断节点保存位置
}
}
}
public void toArrayNode() { //将节点转换为对象数组
if (this.left != null) { //表示有左节点
this.left.toArrayNode(); //左子树继续取得
}
// 先判断左节点再取出中间节点数据,再取得右节点数据
BinaryTree.this.retData[BinaryTree.this.foot++] = this.data;
if (this.right != null) { //表示有右节点
this.right.toArrayNode(); //右子树继续取得
}
}
}
private Node root; //定义根节点
private int count; //保存元素个数
private Object[] retData; //保存返回的对象数组
private int foot; //操作角标
public void add(Object obj) { //进行数据的追加
Comparable com = (Comparable) obj; //转为Comparable才可以实现Node保存
Node newNode = new Node(com); //创建新的节点
if (this.root == null) { //现在不存在节点
this.root = newNode; //保存根节点
} else {
this.root.addNode(newNode); //交给Node类处理
}
this.count++; //保存个数加一
}
public Object[] toArray() { //取得全部保存数据
if (this.root == null) { //根节点为null
return null; //没有数据
}
this.foot = 0;
this.retData = new Object[this.count];
this.root.toArrayNode();
return this.retData;
}
}(3)测试程序,保存多个 Book 类对象。
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree();
bt.add(new Book("Java", 79.8));
bt.add(new Book("c", 79.8));
bt.add(new Book("c++", 79.8));
bt.add(new Book("python", 79.8));
Object[] obj = bt.toArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(obj));
}
}public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree();
bt.add(new Book("Java", 79.8));
bt.add(new Book("c", 79.8));
bt.add(new Book("c++", 79.8));
bt.add(new Book("python", 79.8));
Object[] obj = bt.toArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(obj));
}
}本程序实现了一个最基础的二叉树数据结构,整个程序的实现关键在于 Node 节点大小关系的判断,所以为了实现这一要求,在 Node 中保存的类型为 Comparable 接口类型。
挽救的比较器:Comparator
利用 Comparable 接口实现的比较器属于常见的用法,但是从另外一个角度来讲,如果要使用 Comparable 比较器,就意味着在类定义时必须考虑好排序的需求。但是如果某一个类定义时并没有实现 Comparable 接口,可是在不能修改类定义时又需要进行对象数组排序该怎么办呢?为此,Java 又提供了另外一种比较器: Comparator 接口(挽救的比较器),此接口定义如下。
@FunctionalInterface
public interface Comparator<T> {
public int compare(T o1,T o2);
public boolean equals(Object obj);
}
通过定义可以发现在 Comparator 接口上使用了 @Functionallnterface 注解声明,所以此接口为一个函数式接口。该接口提供了一个compare() 方法,此方法的返回 3 种结果为:1(>0)、-1(<0)、0(=0)。
函数式接口不是应该只有一个方法吗?
回答:Object 类中的方法不属于限定范围。
读者需要注意,虽然 Comparator 接口中定义了两个抽象方法,但是子类真正在覆写时只需要覆写 compare() 方法即可,而 equals() 这样的方法在 Object 类中已经有默认实现(地址比较)。
另外从 Comparator 接口定义之初只定义了 compare() 与 equals() 两个抽象方法,而在 JDK1.8 之后,Comparator 接口中除了抽象方法外也定义了 default 和 static 的普通方法,有兴趣的读者可以自行观察JavaDoc 。
如果要利用 Comparator 接口实现对象数组的排序操作,还需要更换 java.util.Arrays 类中的排序方法。对象数组排序方法为:public static <T> void sort(T[] a,Comparator<? super T> c) 。
(1)定义一个类,此类不实现比较器接口。
package com.yootk.demo;
class Book {
private String title ;
private double price ;
public Book() {}
public Book(String title,double price) {
this.title = title ;
this.price = price ;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "书名:" + this.title + ",价格:" + this.price + "\n" ;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
}package com.yootk.demo;
class Book {
private String title ;
private double price ;
public Book() {}
public Book(String title,double price) {
this.title = title ;
this.price = price ;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "书名:" + this.title + ",价格:" + this.price + "\n" ;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
}(2)假设在 Book 类的初期设计中并没有排序的设计要求,并且不能够修改。但是随着开发的深入,有了对象数组排序的要求,所以此时就可以利用 Comparator 接口单独为 Book 类设计一个排序的规则类:BookComparator 。
class BookComparator implements Comparator<Book> {
@Override
public int compare(Book o1, Book o2) {
if (o1.getPrice() > o2.getPrice()) {
return 1;
} else if (o1.getPrice() < o2.getPrice()) {
return -1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}class BookComparator implements Comparator<Book> {
@Override
public int compare(Book o1, Book o2) {
if (o1.getPrice() > o2.getPrice()) {
return 1;
} else if (o1.getPrice() < o2.getPrice()) {
return -1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}本程序定义了一个 BookComparator 比较器程序类,这样在使用 Arrays.sort() 排序时就需要传递此类的实例化对象。
(3)测试代码,使用指定的比较器,实现对象数组的排序操作。
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Book books [] = new Book [] {
new Book("Java开发实战经典",79.8) ,
new Book("JavaWEB开发实战经典",69.8) ,
new Book("Oracle开发实战经典",99.8) ,
new Book("Android开发实战经典",89.8)
} ;
java.util.Arrays.sort(books,new BookComparator());
System.out.println(java.util.Arrays.toString(books));
}
}public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Book books [] = new Book [] {
new Book("Java开发实战经典",79.8) ,
new Book("JavaWEB开发实战经典",69.8) ,
new Book("Oracle开发实战经典",99.8) ,
new Book("Android开发实战经典",89.8)
} ;
java.util.Arrays.sort(books,new BookComparator());
System.out.println(java.util.Arrays.toString(books));
}
}使用 Comparator 并不像 Comparable 那样方便,所以在利用 Arrays 类实现对象排序时,必须明确设置一个排序规则类的实例化对象后才可以正常完成对象数组的排序功能。
可以使用 Lambda 表达式完成
由于 Comparator 接口上使用了 @Functionallnterface 注解声明,所以用户也可以利用 Lambda 表达式来实现比较规则的定义。
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Book books [] = new Book [] {
new Book("Java开发实战经典",79.8) ,
new Book("JavaWEB开发实战经典",69.8) ,
new Book("Oracle开发实战经典",99.8) ,
new Book("Android开发实战经典",89.8)
} ;
java.util.Arrays.sort(books,(o1,o2)->{
if (o1.getPrice() > o2.getPrice()) {
return 1;
} else if (o1.getPrice() < o2.getPrice()) {
return -1;
} else {
return 0;
}
});
System.out.println(java.util.Arrays.toString(books));
}
}public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Book books [] = new Book [] {
new Book("Java开发实战经典",79.8) ,
new Book("JavaWEB开发实战经典",69.8) ,
new Book("Oracle开发实战经典",99.8) ,
new Book("Android开发实战经典",89.8)
} ;
java.util.Arrays.sort(books,(o1,o2)->{
if (o1.getPrice() > o2.getPrice()) {
return 1;
} else if (o1.getPrice() < o2.getPrice()) {
return -1;
} else {
return 0;
}
});
System.out.println(java.util.Arrays.toString(books));
}
}本程序利用 Lambda 表达式实现了同样的排序操作,这样的代码定义可以节约类的定义,是简化代码的一种有效手段。
请解释 Comparable 和 Comparator 的区别
- 如果对象数组要进行排序就必须设置排序规则,可以使用
Comparable或Comparator接口实现; java.lang.Comparable是在一个类定义时实现好的接口,这样本类的对象数组就可以进行排序,在Comparable接口下定义了一个public int compareTo()方法;java.util.Comparator是专门定义一个指定类的比较规则,属于挽救的比较操作,里面有两个方法:public int compare()、public boolean equals()。